High Availability
This page will describe how to provide high availability (HA) for MAAS at both the rack controller level and the region controller level. See Concepts and terms for detailed information on what services are provided by each of those levels.
Rack controller HA
Although DHCP is handled at the rack controller level one should not worry about a second MAAS-managed DHCP service coming online and causing disruption. DHCP software is added intelligently when a new rack controller is installed and DHCP HA will become available as an option.
Install a second rack controller by reading Rack controller.
BMC HA
HA for BMC control (node power cycling) is provided out of the box once a second rack controller is present. MAAS will automatically identify which rack controller is responsible for a BMC and communication will be set up accordingly.
DHCP HA
DHCP HA affects node management (enlistment, commissioning and deployment). It enables a primary and a secondary DHCP instance to serve the same VLAN where all lease information is replicated between rack controllers. DHCP needs to be MAAS-managed in order for DHCP HA to work.
If DHCP is being enabled for the first time after a second rack controller is added then enable it according to Enabling DHCP.
However, if the initial rack controller already has DHCP enabled then a reconfiguration of DHCP is in order. Simply access the VLAN in question (via the 'Subnets' page) and choose action 'Reconfigure DHCP'. There you will see the second rack controller appearing in the 'Secondary controller' field. All you should have to do is press the 'Reconfigure DHCP' button:
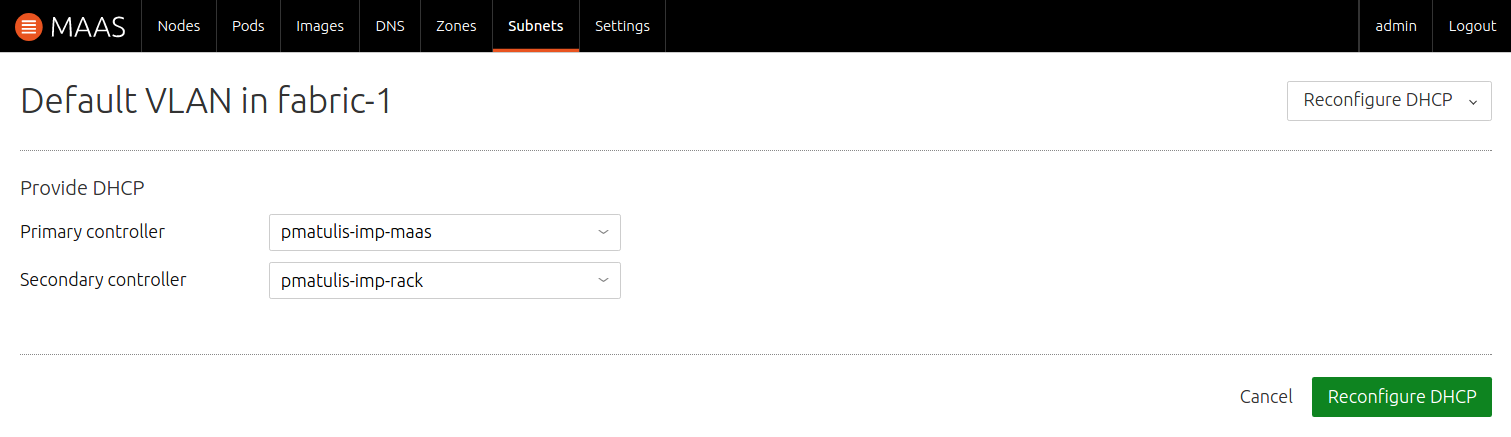
The setup of rack controller HA is now complete.
Region controller HA
Implementing region controller HA involves setting up:
- PostgreSQL HA
- Secondary API server(s)
- Virtual IP address
Load balancing is optional.
PostgreSQL HA
MAAS stores all state information in the PostgreSQL database. It is therefore recommended to run it in HA mode. Configuring HA for PostgreSQL is external to MAAS. You will therefore need to study the PostgreSQL documentation and implement the variant of HA that you feel most comfortable with.
A quick treatment of PostgreSQL HA: hot standby is provided here for convenience only. Its purpose is to give an idea of what's involved at the command line level when implementing one particular form of HA with PostgreSQL.
Note: Each region controller uses up to 40 connections to PostgreSQL in high load situations. Running 2 region controllers requires no modifications to the max_connections in postgresql.conf. More than 2 region controllers requires that max_connections be adjusted to add 40 more connections per extra region controller added to the HA configuration.
Secondary API server
This section assumes that PostgreSQL HA has been set up.
Note: Any number of API servers can be present as long as each connects to the same PostgreSQL database and allows the required number of connections.
On the primary database host, edit file /etc/postgresql/9.5/main/pg_hba.conf
to allow the eventual secondary API server to contact the primary PostgreSQL
database. Include the below line, replacing $SECONDARY_API_SERVER_IP with the
IP address of the host that will contain the secondary API server:
host maasdb maas $SECONDARY_API_SERVER_IP/32 md5
Note: It is very common for the primary database server and the primary API server to reside on the same host.
Apply this change by restarting the database:
sudo systemctl restart postgresql
On a secondary host, add the new API server by installing a few carefully chosen packages:
sudo apt install maas-region-api maas-dns
The /etc/maas/regiond.conf file from the primary API server will be needed.
Below, we assume it can be copied (scp) from the 'ubuntu' account home
directory using password authentication (adjust otherwise). The
local_config_set command will edit that file by pointing to the host that
contains the primary PostgreSQL database. DNS (bind9) configuration options
are also rationalized between bind9 itself and the same options within MAAS:
sudo systemctl stop maas-regiond sudo scp ubuntu@$PRIMARY_API_SERVER:regiond.conf /etc/maas/regiond.conf sudo chown root:maas /etc/maas/regiond.conf sudo chmod 640 /etc/maas/regiond.conf sudo maas-region local_config_set --database-host $PRIMARY_PG_SERVER sudo maas-region edit_named_options --migrate-conflicting-options sudo systemctl restart bind9 sudo systemctl start maas-regiond
Check the log files for any errors:
/var/log/maas/regiond.log/var/log/maas/maas.log/var/log/syslog
Load balancing (optional)
Load balancing can be added with the HAProxy load balancer software.
On each API server host, before haproxy is installed, apache2 needs to be
stopped (and disabled). This is because both apache2 and haproxy listen on the
same port (TCP 80). Recall that Apache is only used to redirect port 80 to port
5240.
sudo systemctl stop apache2 sudo systemctl disable apache2 sudo apt install haproxy
Configure each API server's load balancer by copying the following into
/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg (see the
upstream configuration manual
as a reference). Replace $PRIMARY_API_SERVER_IP and $SECONDARY_API_SERVER_IP
with their respective IP addresses:
frontend maas bind *:80 retries 3 option redispatch option http-server-close default_backend maas backend maas timeout server 90s balance source hash-type consistent server localhost localhost:5240 check server maas-api-1 $PRIMARY_API_SERVER_IP:5240 check server maas-api-2 $SECONDARY_API_SERVER_IP:5240 check
Where maas-api-1 and maas-api-2 are arbitrary server labels.
Now restart the load balancer to have these changes take effect:
sudo systemctl restart haproxy
Virtual IP
A virtual IP (VIP) will be used as the effective IP address of all region API servers. This will be done with the aid of the Keepalived routing software.
On each API server host, install the software, load a kernel module, set it to load upon reboot and pass a kernel option:
sudo apt install keepalived sudo modprobe ip_vs echo 'ip_vs' | sudo tee -a /etc/modules echo 'net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind=1' | sudo tee /etc/sysctl.d/60-keepalived-nonlocal.conf sudo systemctl restart procps
Create the file /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf (see the
keepalived.conf man page as a reference) based on the
example below. Either apache2 or haproxy will be referred to, depending on
whether load balancing (haproxy) was implemented or not (see previous section).
The following variables are used:
- INTERFACE: The network interface (e.g. eth0) from which the API server can be reached by MAAS clients.
- PASSWORD: Participating servers authenticate with one another using this chosen password in order to synchronize. This example uses a cleartext password (auth_type PASS).
- VIP: The virtual IP. This is any IP address available on the subnet.
- PRIORITY: An integer (1-255) that indicates a preference for the corresponding API server to claim the VIP. A larger value indicates a greater preference. For example, the preferred primary could have 150 while the preferred secondary could have 100.
Their values are represented when they are preceded with the '$' character (e.g. $VIP). These are to be replaced with actual values in the file.
### Un-comment next 4 lines if using haproxy
#vrrp_script chk_haproxy {
# script "killall -0 haproxy"
# interval 2
#}
### Un-comment next 4 lines if using apache2
#vrrp_script chk_apache2 {
# script "killall -0 apache2"
# interval 2
#}
vrrp_script chk_named {
script "killall -0 named"
interval 2
}
vrrp_instance maas_region {
state MASTER
interface $INTERFACE
priority $PRIORITY
virtual_router_id 51
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass $PASSWORD
}
track_script {
### Un-comment next line if using haproxy
#chk_haproxy
### Un-comment next line if using apache2
#chk_apache2
chk_named
}
virtual_ipaddress {
$VIP
}
}
Restart the daemon to have these changes take effect:
sudo systemctl restart keepalived
Note: If this is being done inside a container, its host needs the ip_vs module loaded and the sysctl change. A restart of the container will then be required.
Finally, for all API servers, replace the original IP address in the MAAS URL with that of the VIP. Then inform all rack controllers of that change.
To adjust an API server:
sudo maas-region local_config_set --maas-url http://$VIP/MAAS
sudo systemctl restart maas-regiond
To adjust a rack controller:
sudo maas-rack config --region-url http://$VIP/MAAS
sudo systemctl restart maas-rackd
The configuration of region controller HA is now complete.
The API server(s) must be now be referenced (e.g. web UI, MAAS CLI) using port 80 (as opposed to port 5240).
