Zones
The concept of a zone, and examples of how they can be used, are provided in the Concepts and terms page. The current page covers how to use a zone. Specifically, it will show how to:
- Add a zone
- Edit a zone
- Delete a zone
- Assign a node to a zone
- Allocate a node in a zone
All these actions require administrative privileges.
Add a zone
To create a zone, navigate to the 'Zones' page and use the 'Add zone' button. The resulting window will allow for the name and, optionally, a description of the new zone.
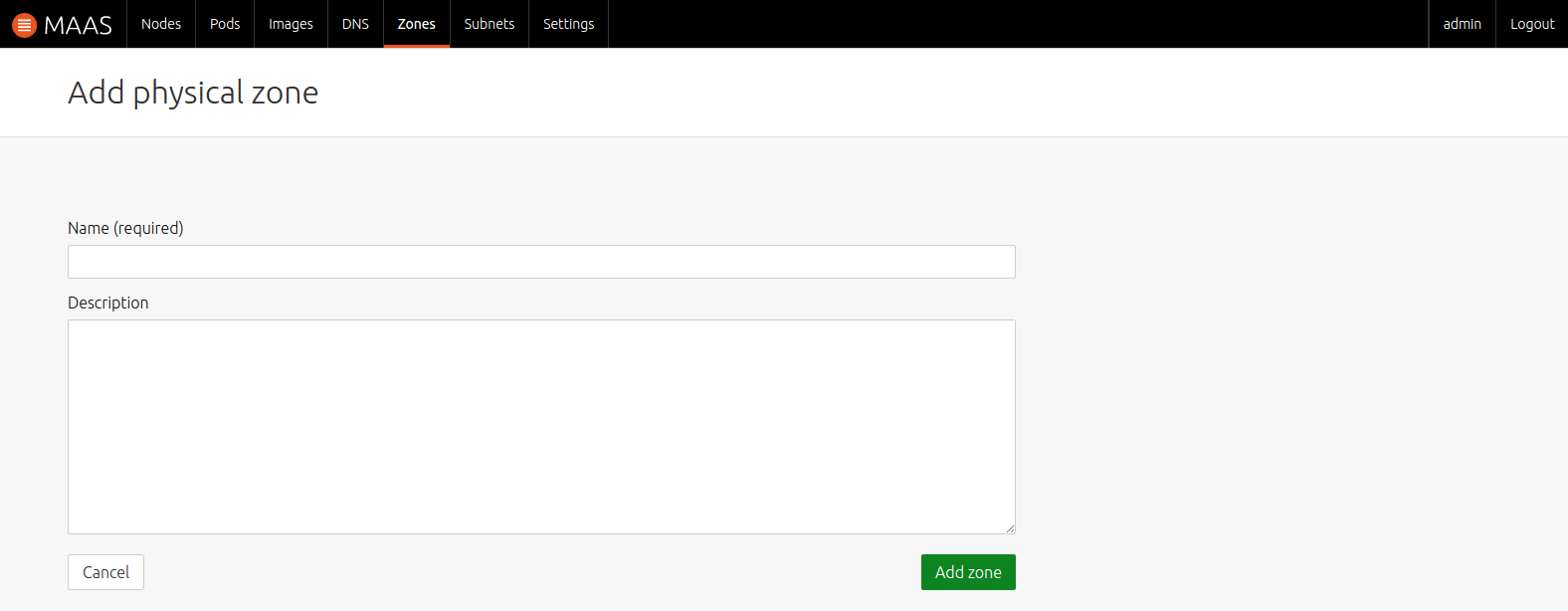
Press the 'Add zone' button to confirm the changes.
Edit a zone
To edit a zone, on the 'Zones' page select a zone and use the 'Edit zone' button. Doing so will allow a change to be made to the name and description.
Delete a zone
To delete a zone, on the 'Zones' page select a zone and use the 'Delete zone' button. Doing so will also move any potential node associations to the default zone.
Assign a node to a zone
To assign a node to a zone, from the 'Nodes' page, select a node (or multiple nodes) and choose 'Set Zone' using the 'Take action' button. After selecting a zone hit the 'Go' button to apply the change.
You can also edit a node's individual page to change its zone.
Both ways are available in the API as well: edit an individual node through a
PUT request to the node's URI, or set the zone on multiple nodes at once by
calling the set_zone operation on the nodes endpoint.
Allocate a node in a zone
To deploy in a particular zone, call the acquire method in the
region-controller API \<region-controller-api> as before, but pass the zone
parameter with the name of the zone. The method will allocate a node in that
zone, or fail with an HTTP 409 ("conflict") error if the zone has no nodes
available that match your request.
Alternatively, you may want to request a node that is not in a particular
zone, or one that is not in any of several zones. To do that, specify the
not_in_zone parameter to acquire. This parameter takes a list of zone
names; the allocated node will not be in any of them. Again, if that leaves no
nodes available that match your request, the call will return a "conflict"
error.
It is possible, though not usually useful, to combine the zone and
not_in_zone parameters. If your choice for zone is also present in
not_in_zone, no node will ever match your request. Or if it's not, then the
not_in_zone values will not affect the result of the call at all.
