Composable Hardware
Composable hardware allows for the dynamic composition of nodes from a pool of available hardware resources (e.g. disk space, memory, cores). MAAS calls such a collection of resources a Pod.
This enables a machine request to be made without having machines pre-built. Modelling tools, such as Juju, can leverage this functionality when requesting a machine from MAAS, which will dynamically create and Deploy one. Machines can also be requested directly from within MAAS.
MAAS currently supports two such architectures:
- Intel Rack Scale Design (RSD)
- Virsh (KVM)
Note: For RSD, MAAS has only been validated to work with Intel RSD reference software release v.1.2.5, based on Redfish API v.1.0 and RSD PODM API v.1.0.
See MAAS CLI - Composable hardware for how to manage composable hardware with the CLI.
Web UI
See Web UI for how to get started with the web UI.
Composable hardware systems are managed on the 'Pods' page, which is initially empty:
Add a Pod
Add/register a Pod by using the 'Add pod' button.
The first example depicts an RSD Pod being added. After choosing 'Rack Scale Design' for 'Pod type' the below form will appear:
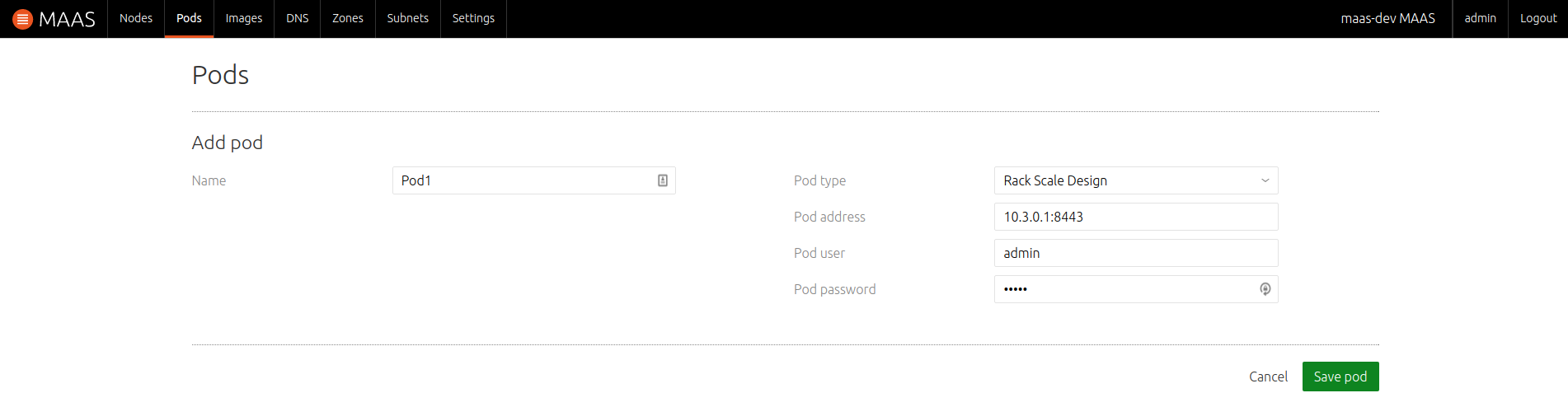
Fill in the fields. You will need to get values for 'Pod address' (IP address or URL followed by a port), 'Pod user', and 'Pod password' from the RSD administrator. Then click 'Save pod'.
Once added, MAAS will automatically discover and store the resources that a Pod contains. Any pre-composed machines will also appear on the 'Nodes' page and be commissioned.
This is how a Virsh Pod is added:
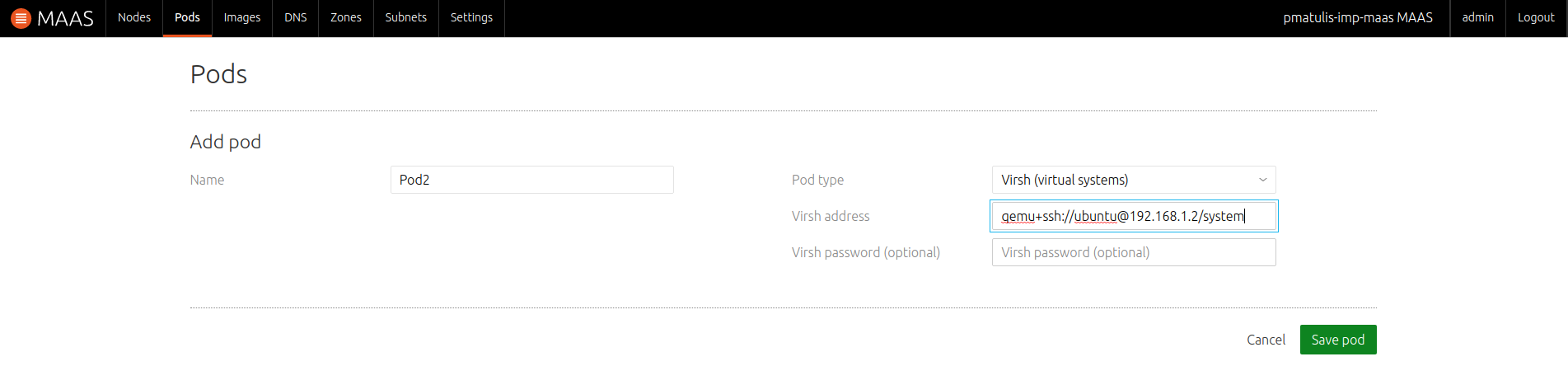
Virsh Pod notes:
- Typically, the KVM host will have a network bridge set up with a libvirt network configured to use it.
- Alternatively, if KVM and MAAS reside on the same system the default NAT libvirt network can be used by disabling DHCP on it and enabling MAAS DHCP on the VLAN associated with the libvirt subnet of 192.168.122.0/24.
- MAAS will first look for a libvirt network named 'maas', then for 'default'.
- KVM guests subsequently created (composed) will not, by default, have a graphics card added at the libvirt level. See LP #1688066.
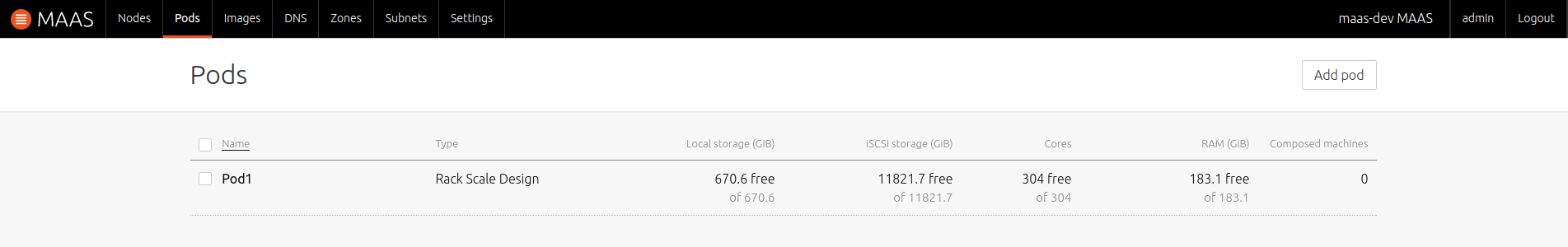
List Pods
The new Pod, including a summary of contained resources, will be listed on the 'Pods' page:
View Pod details
Clicking a Pod's name on the 'Pods' page will reveal the resources contained within it:
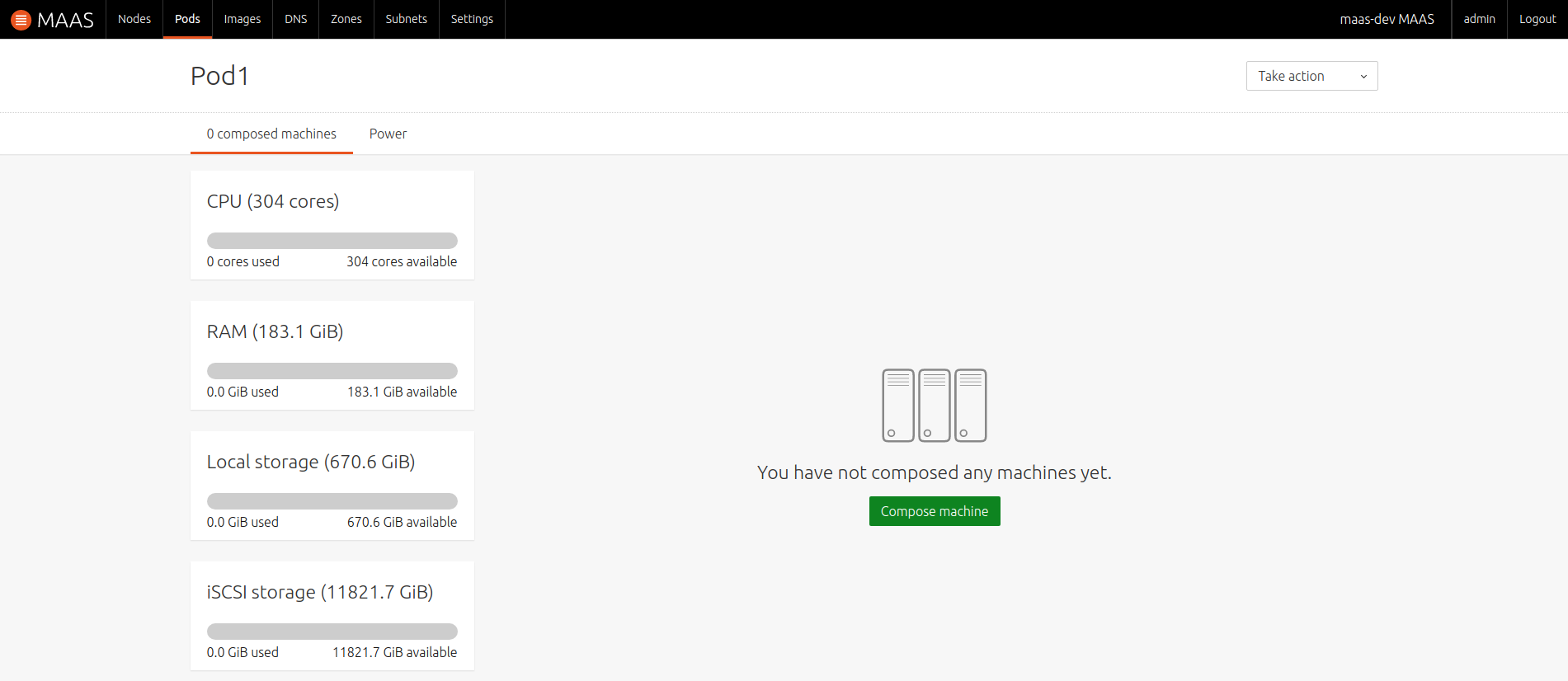
Compose Pod machine
While on a Pod's details view, begin the machine composition process by pressing the 'Compose machine' button:
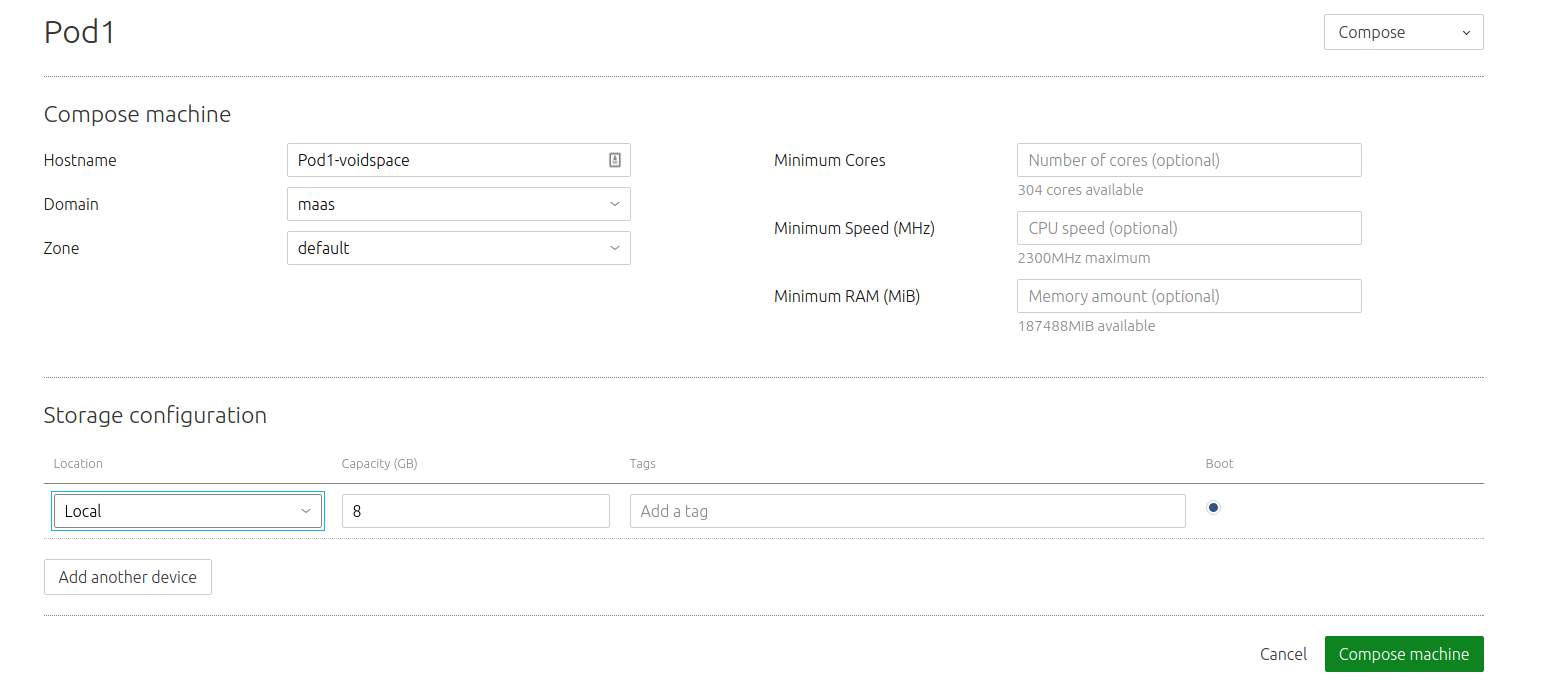
Fill in the fields (many are optional) and hit 'Compose machine' to finish. You will be brought back to the Pod's details view. In a few moments the new machine will be auto-commissioned:
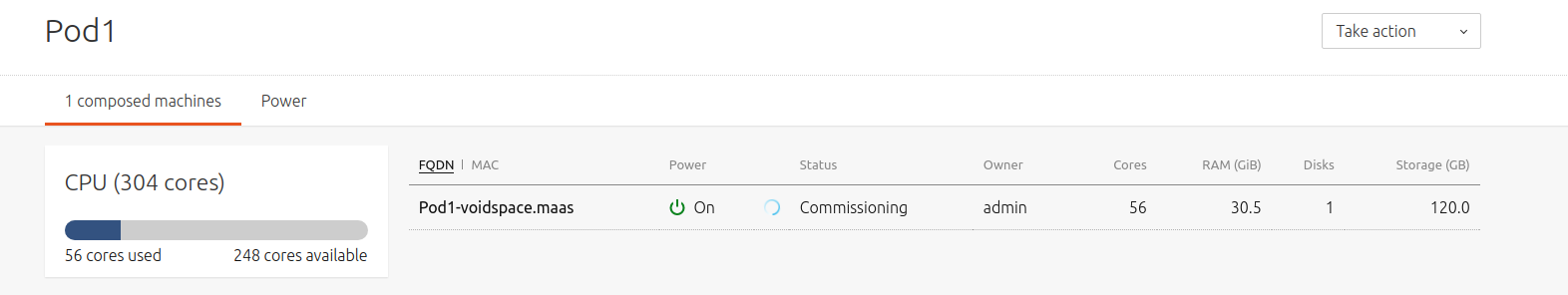
The main 'Nodes' page should reflect this as well.
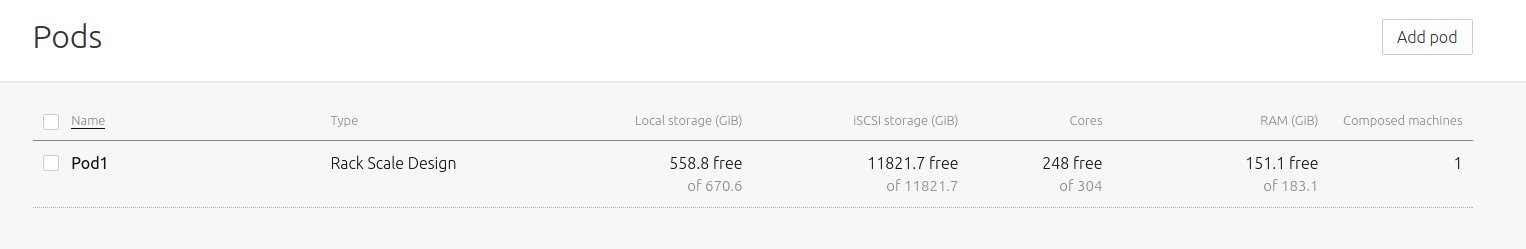
As expected, the new machine's resources will be deducted from the Pod's resources:
Decompose a Pod machine
Decomposing a Pod machine means to send the machine's resources back to the Pod for reuse. Doing so within MAAS will also cause the corresponding MAAS node to be Deleted.
While on a Pod's details view, select the machine to decompose and choose the 'Delete' button from the dropdown menu:
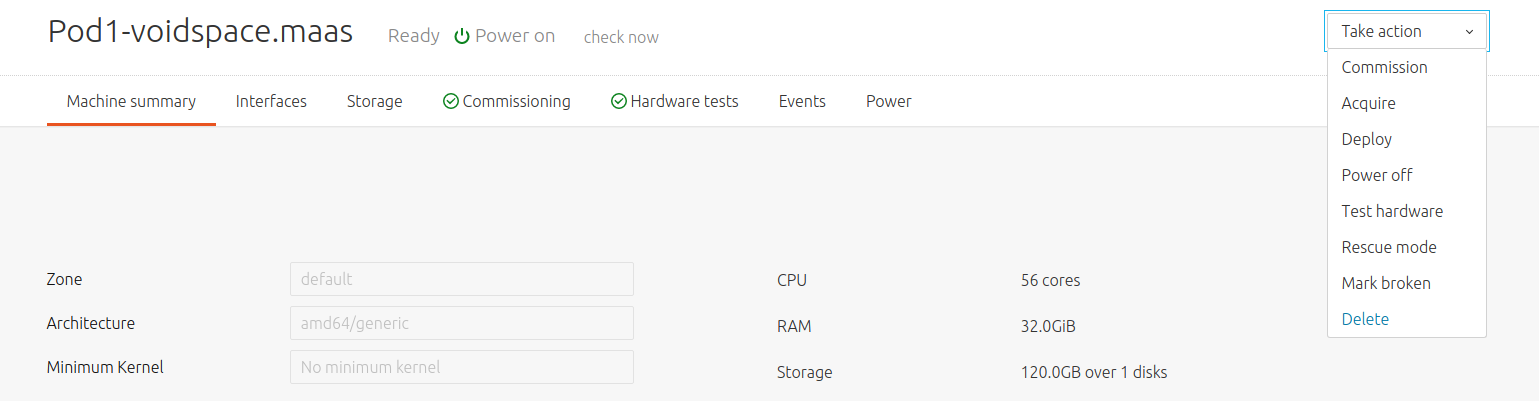
Confirm by hitting the 'Delete machine' button.
Note: This operation can also be achieved by simply deleting the corresponding MAAS node in the regular way.
Once done, you will be transported back to the main 'Nodes' page.
Delete a Pod
While on the main Pods page, select a Pod and choose the 'Delete' action from the dropdown menu. Hit 'Delete 1 pod' to confirm the action:
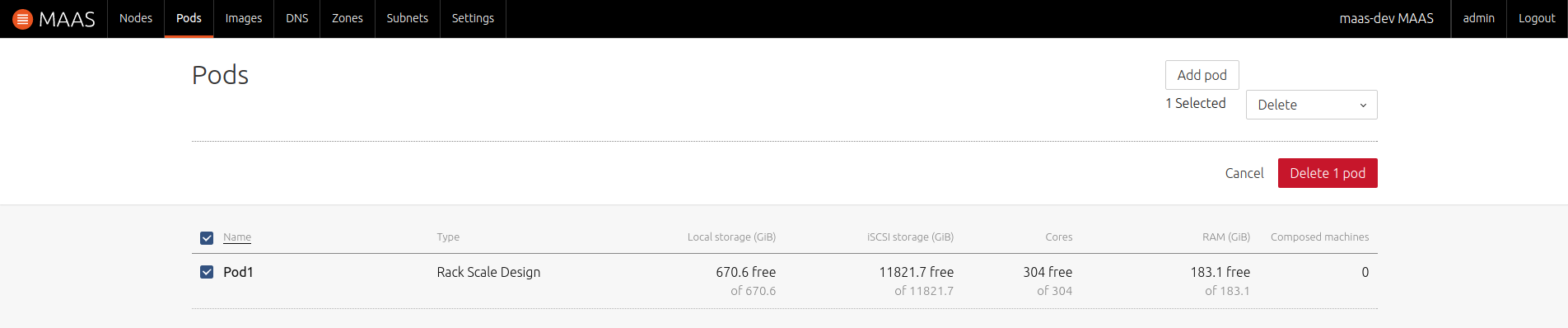
Deleting a Pod will also decompose all its machines, thereby also removing all corresponding nodes from MAAS.
