Commissioning and Hardware Testing Scripts
MAAS runs various scripts during enlistment, commissioning and testing to collect data about nodes. Commissioning scripts are used to configure hardware or perform other tasks during commissioning, such as updating firmware, whereas hardware testing scripts are used to evaluate system hardware and report its status.
Note: MAAS runs built-in commissioning scripts only during enlistment. Custom commissioning scripts are only run when commissioning is explicitly run.
Scripts can be selected to run from web UI during commissioning, by testing hardware or from the command line.
This page explains the various metadata fields used within these scripts, how parameters are passed to scripts and how any results are returned, along with examples of both commissioning and hardware testing scripts.
Note: By default, all commissioning scripts will be run except those which use the for_hardware feature. Similarly, any test script tagged commissioning using the script_type parameter will be run during commissioning or testing. See below for more details.
A typical administrator workflow (with node states) using customised commissioning scripts is represented here:
Add node -> Enlistment (runs built-in commissioning scripts MAAS) -> New -> Commission (runs built-in and custom commissioning scripts) -> Ready -> Deploy
Note: In subsequent releases of MAAS, administrators will be able to make a machine 'Ready' simply by running hardware tests. For now, administrators will need to Commission the new machine.
Metadata fields
Metadata fields tell MAAS when the script should be used, how it should be run, and what information a script is gathering. A script can have the following fields:
name: The name of the script.title: Human-friendly descriptive version of name, used within the web UI.description: Brief outline of what the script does.tags: List of tags associated with the script.type: Either commissioning or testing.timeout: Length of time before MAAS automatically fails and kills execution of the script. The time may be specified in seconds or using the HH:MM:SS format.destructive: True or False, depending on whether the script will overwrite system data. Destructive tests can not be run on a deployed machine.comment: Describes changes made in this revision of the script.hardware_type: Defines the type of hardware the script configures or tests. If the script returns results, hardware type dictates what hardware the results are associated with. The following types are valid:node: Not associated with any hardware type. This is the default.cpu: Configures or tests the CPUs on the node.memory: Configures or tests memory on the node.storage: Configures or test storage on the node. Each storage result may be associated with a block device on the system.
parallel: Enables scripts to be run in parallel and can be one of the following:disabled: The script will run serially on its own.instance: Runs in parallel only with other instances of the same script.any: Runs in parallel alongside any other scripts with parallel set to any.
parameters: What parameters the script accepts.results: What results the script will return.packages: List of packages to be installed or extracted before running the script. Packages may be specified as a JSON string, a list of strings, or as a dictionary. For example,packages: {apt: stress-ng}, would askaptto install stress-ng. Package sources can be any of the following:apt: Used by default if the source is omitted.snap: Installs packages using [snap][snapcraft]. May also be a list of dictionaries. The dictionary must define the name of the package to be installed, and optionally, thechannel,modeandrevision.url: The archive will be downloaded and, if possible, extracted or installed when a Debian package or [snap][snapcraft].
for_hardware: Specifies the hardware that must be on the machine for the script to run. May be a single string or list of strings of the following:modalias: Starts with 'modalias:' may optionally contain wild cards.PCI ID: Must be in the format of 'pci:VVVV:PPPP' where VVVV is the vendor ID and PPPP is the product ID.USB ID: Must be in the format of 'usb:VVVV:PPPP' where VVVV is the vendor ID and PPPP is the product ID.System Vendor: Starts with 'system_vendor:'.System Product: Starts with 'system_product:'.System Version: Starts with 'system_version:'.Mainboard Vendor: Starts with 'mainboard_vendor:'.Mainboard Product: Starts with 'mainboard_product:'.
may_reboot: When True indicates to MAAS the script may reboot the machine. MAAS will allow up to 20 minutes between heartbeats while running a script withmay_rebootset to True.recommission: After all commissioning scripts have finished running rerunscript_type: commissioning or test. Indicates whether the script should be run during commissioning or hardware testing.
Parameters
Scripts can accept values defined within the parameters field. Parameters are
automatically filled by MAAS to allow one test to be run against multiple
devices at once while keeping seperate logs.
Parameters may only be defined within the embedded YAML of the script, and they take the form of a dictionary of dictionaries.
The key of the dictionary must be a string and it's this string that's used by the UI and API when users are setting parameter values during commissioning or testing.
The value is a dictionary with the following fields:
type: Every parameter must contain a type field. This describes what the parameter may accept and its default values. It may be one of the following:storage: Allows the selection of a strong device on the node being run.
title: The title of the parameter field when displayed in the UI. The following types have the following default values:storage: Storage device.
argument-format: Specifies how the argument should be passed to the script. Input is described as{input}. The storage type may also use{name},{path},{model}or{serial}. MAAS will lookup the values of path, model, and serial based on user selection. For storage,{input}is synonymous with{path}. The following types have the following default values:storage:--storage={path}
default: The default value of the parameter. The following types have the following default values. Setting these to '' or None will override these values:storage: all.
required: Whether or not user input is required. If set to false, no default is set and no user input will mean the parameter is not passed to the script. Defaults totrue.results: What results the script will return on completion. This may only be defined within the embedded YAML of the script. Results may be a list of strings or a dictionary of dictionaries.
Example script using default values:
#!/usr/bin/env python3 # --- Start MAAS 1.0 script metadata --- # name: example # parallel: instance # parameters: # storage: {type: storage} # --- End MAAS 1.0 script metadata --- import argparse parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='') parser.add_argument( '--storage', dest='storage', required=True, help='path to storage device you want to test. e.g. /dev/sda') args = parser.parse_args() print("Testing: %s" % args.storage)
Example script using customized paramaters:
#!/bin/bash # --- Start MAAS 1.0 script metadata --- # name: example # parallel: instance # parameters: # storage: # type: storage # argument-format: '{model}' '{serial}' # --- End MAAS 1.0 script metadata --- echo "Model: $1" echo "Serial: $2"
Environment variables
The following environment variables are available when a script is run within the MAAS environment:
OUTPUT_STDOUT_PATH: The path to the log of STDOUT from the script.OUTPUT_STDERR_PATH: The path to the log of STDERR from the script.OUTPUT_COMBINED_PATH: The path to the log of the combined STDOUT and STDERR from the script.RESULT_PATH: Path for the script to write a result YAML to.DOWNLOAD_PATH: The path where all files have been downloaded to.RUNTIME: The amount of time the script has to run in seconds.HAS_STARTED: When True MAAS has run the script once before but not to completion. Indicates the machine has been rebooted.
Results
A script can output its results to a YAML file and those results will be associated
with the hardware type defined within the script. The path for the results file
is provided by MAAS in an environment variable, RESULT_PATH. Scripts should
write YAML to this file before exiting.
If the hardware type is storage, for example, and the script accepts a storage type parameter, the result will be associated with a specific storage device.
The YAML file must represent a dictionary with the following fields:
result: The completion status of the script. This can be eitherpassed,failed,degraded, orskipped. If no status is defined, an exit code of0indicates a pass while a non-zero value indicates a failure.results: A dictionary of results. The key may map to a results key defined as embedded YAML within the script. The value of each result must be a string or a list of strings.
Optionally, a script may define what results will be returned in the YAML file in the
Metadata fields. The results field should contain a dictionary
of dictionaries. The key for each dictionary is a name which will be returns by the
results YAML. In each dictionary the following fields may be defined:
title- The title for the result which will be used in the UIdescription- The description of the field used as a tooltip in the UI.
Example degrade detection:
#!/usr/bin/env python3 # --- Start MAAS 1.0 script metadata --- # name: example # results: # memspeed: # title: Memory Speed # description: Bandwidth speed of memory while performing random read writes # --- End MAAS 1.0 script metadata --- import os import yaml memspeed = some_test() print('Memspeed: %s' % memspeed) results = { 'results': { 'memspeed': memspeed, } } if memspeed < 100: print('WARN: Memory test passed but performance is low!') results['status'] = 'degraded' result_path = os.environ.get("RESULT_PATH") if result_path is not None: with open(result_path, 'w') as results_file: yaml.safe_dump(results, results_file)
Script examples
Built-in scripts
The source to all commissioning and test scripts can be downloaded at any time over the API
maas $PROFILE node-script download $SCRIPT_NAME
The source code to all built-in scripts is available on launchpad.
Commissioning script: Configure HPA
Below is a sample script to configure an Intel C610/X99 HPA controller on an HP system. The script will only run on systems with an Intel C610/X99 controller identified by the PCI ID 8086:8d06.
Before the script runs, MAAS will download and install the HP RESTful Interface Tool package from HP. After the script successfully completes, the built-in commissioning scripts will be re-run to capture the new configuration.
#!/bin/bash -ex # --- Start MAAS 1.0 script metadata --- # name: hp_c610_x99_ahci # title: Configure Intel C610/X99 controller on HP systems # description: Configure Intel C610/X99 controller on HP systems to AHCI # script_type: commissioning # tags: configure_hpa # packages: # url: http://downloads.linux.hpe.com/SDR/repo/hprest/pool/non-free/hprest-1.5-26_amd64.deb # for_hardware: pci:8086:8d06 # recommission: True # --- End MAAS 1.0 script metadata --- output=$(sudo hprest get EmbeddedSata --selector HpBios.) echo $output if [ $(echo $output | grep -c 'EmbeddedSata=Raid') ]; then echo "Server is in Dynamic Smart Array RAID mode. Changing to SATA AHCI support mode." sudo hprest set EmbeddedSata=Ahci --selector HpBios. --commit else: echo "No changes made to the system, Server is Already in AHCI Mode" fi
Commissioning script: Update firmware
Below is a sample script to update the mainboard firmware on an ASUS P8P67 Pro using a vendor provided tool. The tool will be automatically downloaded an extracted by MAAS. The script reboots the system to complete the update. The system will boot back into the MAAS ephemeral environment to finish commissioning and optionally testing.
Note: Vendor tools which use UEFI boot capsules or need to store resource files on disk while rebooting are not currently supported.
#!/bin/bash -ex # --- Start MAAS 1.0 script metadata --- # name: update_asus_p8p67_firmware # title: Firmware update for the ASUS P8P67 mainboard # description: Firmware update for the ASUS P8P67 mainboard # script_type: commissioning # tags: update_firmware # packages: # url: http://example.com/firmware.tar.gz # for_hardware: mainboard_product:P8P67 PRO # may_reboot: True # --- End MAAS 1.0 script metadata --- $DOWNLOAD_PATH/update_firmware reboot
Hardware test script: CPU stress test
As a simple example, here's a functional Bash script replicating part of the stress-ng script bundled with MAAS:
#!/bin/bash -e # --- Start MAAS 1.0 script metadata --- # name: stress-ng-cpu-test # title: CPU validation # description: Run stress-ng memory tests for 5 minutes. # script_type: test # hardware_type: cpu # packages: {apt: stress-ng} # tags: cpu # timeout: 00:05:00 # --- End MAAS 1.0 script metadata --- sudo -n stress-ng --matrix 0 --ignite-cpu --log-brief --metrics-brief --times \ --tz --verify --timeout 2m
The above Bash script contains comment-delineated metadata that configures the script environment and installs any dependencies, plus a single line of functionality that runs stress-ng (a CPU stress-test utility) with various arguments.
Automatic script selection by hardware type
When selecting multiple machines in the web UI, scripts which
declare the for_hardware field will only run on machines with matching
hardware. To automatically run a script when 'Update firmware' or 'Configure
HBA' is selected the script must be tagged with 'update_firmware' or
'configure_hba'.
Similarly, scripts selected by tag on the command line
which specify the for_hardware field will only run on matching hardware.
Upload procedure
Scripts can be uploaded to MAAS using the web UI. Select the 'User scripts' tab of the 'Settings' page - the 'Commissioning scripts' section is near the top. Within the Commissioning scripts section, click the Upload script button followed by 'Choose file' to open a requester, locate the script, and select Upload to upload it to MAAS.
A status message of Commissioning script created will appear and you'll now be able to select your script after selecting Test hardware from a machine's 'Take action' menu.
Note: MAAS executes scripts in lexicographical order. This allows you to control when your scripts are executed and if they run before or after the standard MAAS scripts.
Debugging
Clicking on the title of a completed or failed script will reveal the output from that specific script.

If you need further details, especially when writing and running your own scripts, you can connect to a node and examine its logs and environment.
To do this, enable Allow SSH access and prevent machine from powering off when selecting 'Test hardware' from the machine 'Take action' menu.
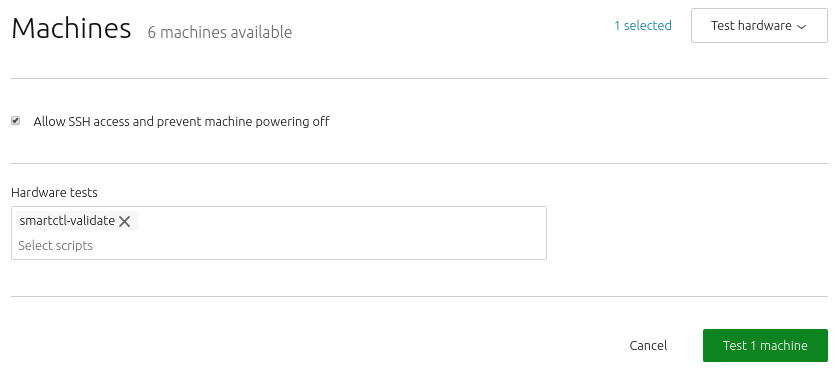
Because scripts operate within an ephemeral version of Ubuntu, enabling this option stops the node from shutting down, allowing you to connect and probe a script's status.
As long as you've added your SSH key to MAAS, you can simply
connect with SSH to the node's IP with a username of ubuntu. Type sudo -i
to get root access.
Access individual scripts and log files
Commissioning and testing script files
/tmp/user_data.sh.*/scripts/commissioning/: Commissioning scripts/tmp/user_data.sh.*/scripts/testing/: Hardware testing scripts
Log files
/tmp/user_data.sh*/out//var/log/cloud-init-output.log/var/log/cloud-init.log
Run all scripts manually
You can also run all commissioning and hardware-testing scripts on a machine for debugging.
/tmp/user_data.sh.*/bin/maas-run-remote-scripts \ [--no-download] \ [--no-send] \ /tmp/user_data.sh.*
Where:
--no-download: Optional. Do not download the scripts from MAAS again.--no-send: Optional. Do not send the results to MAAS.
For example, to run all the scripts again without downloading again from MAAS:
/tmp/user_data.sh.*/bin/maas-run-remote-scripts --no-download /tmp/user_data.sh.*
Here, all the scripts are run again after downloading from MAAS, but no output data is sent to MAAS:
/tmp/user_data.sh.*/bin/maas-run-remote-scripts --no-send /tmp/user_data.sh.*
Command line access
For information about managing scripts, applying tags to scripts and seeing script results using the CLI, please see CLI Hardware Testing Scripts.
